A typical flower consists of different parts. Observe the stems and leaves.
Parts Of A Flower An Illustrated Guide Amnh
As a kid I was never much of a hiker but now I love spending an hour hiking trails.

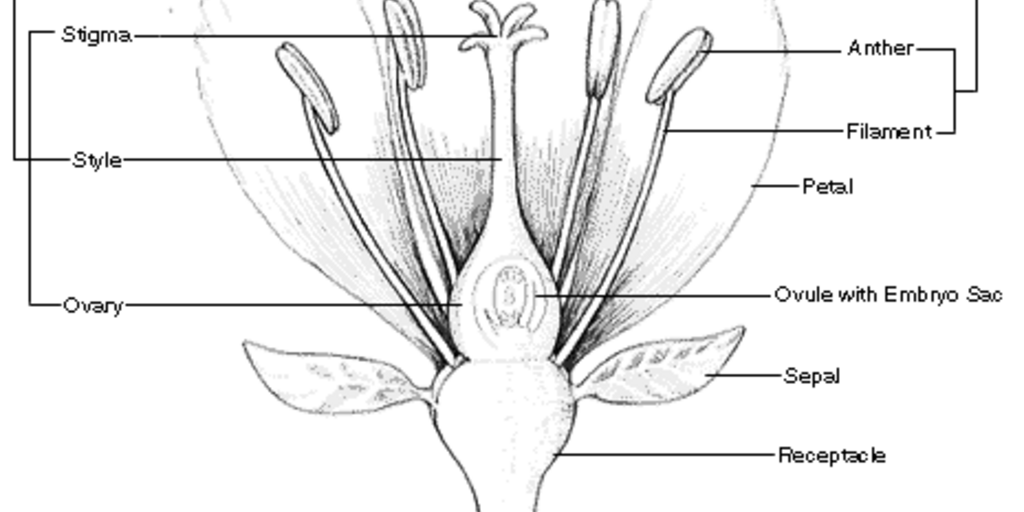
What are the parts of the flower called. This is called the calyx. Androecium and gynoecium are reproductive structures. Therefore it is important to know about the parts that make a flower as they all contribute in these processes.
Apart from these basic parts a. The stalk of flower is called pedicel. In a flower the female reproductive part is called the Pistil.
A flower has both vegetative and reproductive partsThe major parts of a flower are. A typical diagram of a flower is divided into four main parts. The expanded tip of the pedicel from where the floral parts arise is called thalamus.
The stigma style and ovary. Inside the corolla are the pistils stamens and sepals that surround the flower organs. A typical diagram of a plant body consists of three parts.
Sepals protect the flowers before they bloom. As the flower head matures the flower petals wither and are pushed off the plant by the emerging seeds. As the hibiscus begins to bloom the petals begin to grow.
At the bottom of every hibiscus bud is a green structure at the top of the stem. The older I get the more I appreciate the beauty of nature. Includes 7 anatomy illustrations of the flower stem plant cell leaf plant structure chloroplast photosynthesis process and more.
Each seed develops a white umbrellalike tuft sometimes called a parachute that is instrumental in helping the plant to propagate. Many different species of lilies are grown so their stems and leaves. The bloom is part of the flower with leaves and petals.
The receptacle also called the floral axis or thalamus is generally very small. When a flower has all the four floral parts it is called a complete flower. Sepals may be united gamosepalous or free polysepalous.
It has three main parts called stigma style and ovary. The flower is the modified shoot for reproduction. Species have separate male and female flowers and an individual flower can be missing some parts Tell children that although all of them have the same parts-- nose eyes arms legs hair etc-- they too are all unique.
Calyx corolla androecium and gynoecium Among these calyx and corolla are vegetative structuresThey are called the non-essential whorls. Those with only female parts are called carpellate or pistillate flowers. Rather than just roots a lily has a bulb on the bottom.
The pistil is comprised of three parts. A flower missing any one of them is. Most flowers have male and female parts that allow the flower to produce seeds.
A flower can have more than one bloom on the stem. The outer parts of the flower often green and leaf-like that enclose a developing bud. Some flower parts are solitary while others may form a tight spiral or whorl around the flower stem.
Flowers contain vital parts including petals which form flowers. The pistil resides in the middle of the flower. The parts of a flower that are often conspicuously colored.
The Parts of a Lily Flower Bulb. The part of a flower stalk where the parts of the flower are attached. 1 roots 2 stems and 3 leaves each having specialized functions.
The floral parts are arranged at the end of a stem without any internodes. The pollen producing part of a flower usually with a slender filament supporting the anther. The female part of the flower is called the carpel or pistil.
The part of the stamen where pollen is produced. Point out the petals of. Every flower has multiple petals which differ in.
Flowers can have male parts female parts or both. The ultimate guide to the different parts of a flower and plant. Along with the vegetative and reproductive parts a flower is also composed of four whorls which are largely responsible for the radial arrangement of a flower.
What Are the Parts of a Hibiscus Flower. It is the first whorl containing sepals. Look at the bottom of a whole lily plant.
Most seeds transform into fruits and vegetables. Learn more about the main parts of a flower. The petals form a ring called the corolla.
1 sepals 2 petals 3 stamen and 4 carpel each of them performing distinct functions. A typical flower has a circular section with a common centre which can be clearly observed and distinguished from the top of. The anthers or male part of the flower that produces pollen matures before the stigma the female part of the flower that accepts the pollen.
Have learners choose a flower and sketch it on the Parts of a Flower. Stamen is the male reproductive part of a flower.
The leading strand is created continuously making one long strand. A sugar molecule a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base.

The Structure Of Dna By Ron Vale Genetics The Structure Of Dna
Each daughter DNA molecule is composed of one parental strand and one new strand Which of the following structural characteristics of DNA explains its ability to store genetic information.
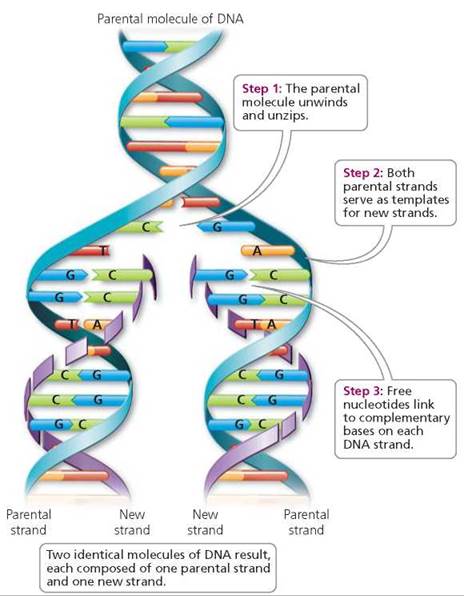
What is the new strand of dna called. The clusters are provided by an enzyme called DNA primase which is a type of dependent-RNA polymerase DNA. The nitrogenous base of a DNA nucleotide can be one of four different molecules. The enzyme joins nucleotides to synthesize a new complementary strand of DNA.
The two strands of DNA run in opposite directions to each other and are thus antiparallel. The process of replication that is the formation of new DNA strands is carried out by a class of enzymes called DNA polymerases. The short lagging strand fragments are called Okazaki fragments.
This sort of DNA replication is continuous. The continuously synthesized DNA strand is called the leading strand and the discontinuously synthesized strand is called the lagging strand. This short segment is called the primer which consists of nine to twelve nucleotides.
The double-stranded DNA molecule is split apart and RNA Pol binds to one strand which it will read and copy. These building blocks are made of three parts. A phosphate group a sugar group and one of four types of nitrogen bases.
Lagging Strand-----There is the lagging strand and the leading strand when DNA is replicated at the fork. The leading strand is the strand of new DNA which is synthesized in the same direction as the growing replication fork. The sugar in DNA is 2-deoxyribose which is a pentose five- carbon sugar.
Each strand of DNA is a polynucleotide composed of units called nucleotides. DNA replication is called semiconservative because each new DNA molecule is made up of one original and one new strand. The principal enzyme involved in DNA replication is called DNA polymerase.
The sugar in DNAs nucleotides is called deoxyriboseDNA is an abbreviation for deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is made of chemical building blocks called nucleotides. RNA molecules use a different sugar called ribose.
This strand is called the template strand or the anti-sense. Each DNA strand of a progenitor cell serves as a. The lagging strand is made of many small fragmentspieces called Okazaki fragments and is generated discontinuously not as one long strand but pieces.
These strands of DNA are called chromatin. To form a strand of DNA nucleotides are linked into chains with the phosphate and sugar groups alternating. A biopolymer comprising multiple linked nucleotides as in DNA is called a polynucleotide.
Similarly what does each DNA strand represent. Attached to each sugar is one of four types of nucleobases informally bases. Why is DNA replication called semi-conservative.
A nucleotide has three components. The lagging strand is the strand of new DNA whose direction of synthesis is opposite to the direction of the growing replication fork. Which of the following builds new strands of DNA the process synthesizes a short range of RNA to an available DNA strand.
Sign in to download full-size image Figure 2. It is done by an enzyme called RNA Polymerase RNA Pol. Remember that during interphase the DNA is contained in the nucleus and consists of very long strands of DNA.
The two DNA strands are also known as polynucleotides as they are composed of simpler monomeric units called nucleotides. The DNA component the team identified is called the intercalated motif i-motif structure which was first discovered by researchers in the 1990s but up until now had only ever been witnessed in vitro not in living cells. RNA Pol only reads one of the two DNA strands as it makes the RNA molecule.
The backbone of the DNA strand is made from alternating phosphate and sugar groups. Adenine A guanine G thymine T and cytosine C.
The part of the foot which joins it to the leg is called the heel. Foot part 4 Back of the foot 4 Command to Rover 4 Part of foot 6 INSTEP.

Anatomy Of The Foot And Ankle Orthopaedia
The word that solves this crossword puzzle is 6 letters long and begins with A.

Parts of feet called. Covers the end of the top of the toes. Curve over 4 Curved structure 4 Something curved 4 Footwear insert 4 Curved span 4 Part of foot 4 HEEL. The hard foot of an ungulate is a hoof.
The outsole of the foot is the part on the bottom of the shoe that touches the ground. Is the back part of the foot below the ankle. Unlike calluses corns have a central core or spot in the middle that is surrounded by dead skin.
Additionally the lower leg often refers to the area between the knee and the ankle and this area is critical to the functioning of the foot. This consists of five long metatarsal bones and five shorter bones that form the toes phalanges. The talus forms a joint with four bones.
Best Answer for Parts Of Feet Crossword Clue. In humans the foot is one of the most complex structures in the body. The insides of your feet correlate to your spine.
The padded portion foot between the toes and the arch. Foot dysfunctions like heel spurs are most common in people who have plantar fasciitis inflammation of the fascia on the sole of the foot. The foot is divided into three sections - the forefoot the midfoot and the hindfoot.
It is made up of over 100 moving parts bones muscles tendons and ligaments designed to allow the foot to balance the bodys weight on just two legs and support. The foot is a part of vertebrate anatomy which serves the purpose of supporting the animals weight and allowing for locomotion on land. Where the bottom of the foot curves.
Tibia fibula calcaneus and navicular. A softer sole provides greater ability to absorb shock. Parts of your foot correlated with the stomach are found above the waistline.
Thus they define the boundaries of the three muscle compartments of the sole see below. The foot contains a lot of moving parts - 26 bones 33 joints and over 100 ligaments. A common one is the development of bony growths on the underside of the calcaneus called heel spurs that cause severe pain when standing or walking.
The feet of monkeys are much like the hands. The foot diagram has a complex structure made up of bones ligaments muscles and tendonsUnderstanding the structure of the foot is best done by looking at a foot diagram where the anatomy has been labeled. Parts correlated with the intestines are found below.
Most land vertebrates have feet and there are many different sorts of foot. The cuboid is on the lateral side of the foot outer foot and sits in front of the calcaneus. See below flat feet or high arches.
Part of foot 4 ARCH. The other bones of the foot. A higher heel places more pressure on the balls of the feet and toes.
Foot part 6 Part of foot 3 TOE. Calluses are thickened areas of skin over parts of the feet where excessive amounts of pressure or friction occur. The heel gives the shoe elevation.
The thinnest part of your foot usually found towards its center is known as the waistline. These make up the toes and broad section of the feet. The foot is traditionally divided into three regions.
The bones of the foot are organized into rows named tarsal bones metatarsal bones and phalanges. The navicular is on the medial inner side of the foot between the talus and the cuneiform bones in front. The bottom of the foot is called the sole.
The central component of this tissue extends to the supporting bones and gives two divisionsthe medial component and lateral component. Corns occur on the toes where they rub against the shoe. The sole and the longitudinal arch of the foot are supported by a thick connective tissue the plantar fascia.
The 26 bones of the foot consist of eight distinct types including the tarsals metatarsals phalanges cuneiforms talus navicular and cuboid bones. The bottom back part of the shoe is called the heel. The padded portion of the sole of the human foot between the toes and the arch.
The area just underneath your toes corresponds to the chest. The hindfoot the midfoot and the forefoot Figure 2. If you would like to learn all the parts of.
Pedal digit 3 Foot part 3 Foot digit 3 Shoe part 3 Gout target usually 3 Body part with a nail 3. The skeletal structure of the foot is.
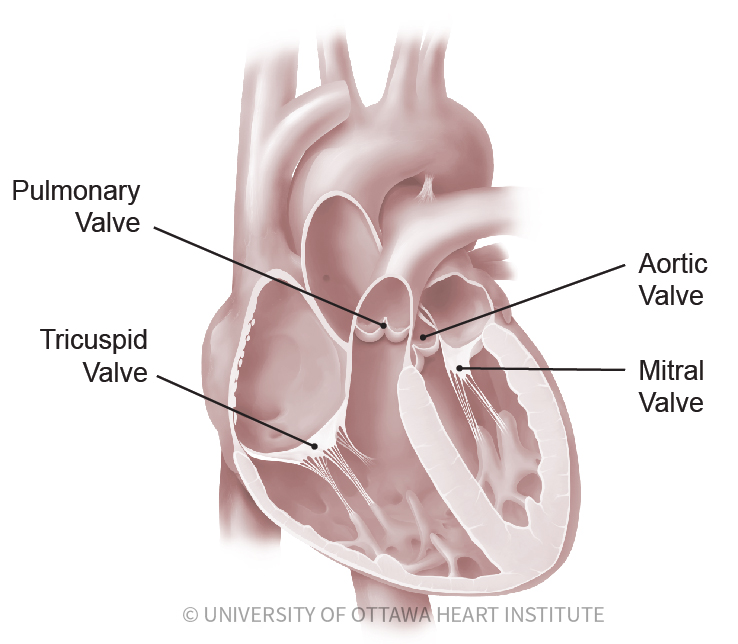
There are four heart valves in a healthy human heart. The valves help to maintain proper blood flow through the heart keeping blood moving efficiently and smoothly and in the right direction.
After passing through the tricuspid valve blood.
What are the four heart valves called. All four valves open and close to help move blood from one area to another. Good morning Dhruval Thank you for asking me. The leaflets open to let blood move forward through the heart during half of the heartbeat.
The valves are made of strong thin flaps of tissue called leaflets or cusps. Types of heart valves. The heart valves play a vital role in the function of the heart.
Normal valves have 3 flaps leaflets except the mitral valve. The tricuspid valve lies between the right atrium and the right ventricle and opens to allow blood to flow into the right ventricle from the right atrium. Keep reading to know more about these four valves and their functioning.
The left side of the heart can be thought of as the hearts powerful engine. Causes of recurrent boils. The 4 heart valves are.
The tricuspid valve is the first of the heart valves through which blood flows to the. The four valves in order of circulation are. The mitral valve and tricuspid valve are located between the atria upper heart chambers and the ventricles lower heart chambers.
Tricuspid valve located between the right atrium and right ventricle Pulmonary or pulmonic valve between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. The four heart valves are. Each side of the heart has a collecting chamber on top atrium and a pumping chamber on the bottom ventricle.
These valves are actual flaps that are located on each end of the two ventricles lower chambers of the heartThey act as one-way inlets of blood on one side of a ventricle and one-way outlets of blood on the other side of a ventricle. CHD a prior heart attack uncontrolled hypertension abnormal heart valves congenital heart disease heart defects present at birth and heart muscle disease. There is a valve between the upper and lower chamber and there is a valve between the lower pumping chamber and the body.
The valves prevent the backward flow of blood. The four valves of the heart include the tricuspid valve the mitral vale the pulmonary valve and the aortic valve. Conditions that can be associated with the development of heart failure include.
The tricuspid valve is named because it has three flaps called cusps or leaflets. I am a bit perplexed by the variety of topics in medicine and in the complexity or otherwise of your Qs. The four types of heart valves play an important role in ensuring that blood flows in only one direction and they are as follows.
Has three leaflets or cusps. Normally the mitral valve closes just before the tricuspid valve and when the two different sounds are detectable it is called a split S1 A split S1 may be indicative of certain conditions affecting the heart. In addition to the valves there are four heart chambers the upper chambers are called the left and right atria the lower chambers are the left and right ventricle.
The heart has four valves - one for each chamber of the heart. Separates the top right chamber right atrium from the bottom right chamber right ventricle. The four heart valves make sure that blood always flows freely in a forward direction and that theres no backward leakage.
The first sound S1 is generated by vibrations created by the closing of these two valves. There are 4 valves of the heart 2 on the left side and 2 on the right side. I thought initially that you might be a medical student but from the very empirical nature of.
Valves are actually flaps leaflets that act as one-way inlets for blood coming into a ventricle and one-way outlets for blood leaving a ventricle. Two of the valves the mitral and the tricuspid valves move blood from the upper chambers of the heart the atria to the lower chambers of the heart the ventricles. The heart has four heart valves the aortic mitral pulmonary and tricuspid valves.
Blood flows through this valve after leaving the right atrium. They close to keep blood from flowing backward during the other half of the heartbeat. The valves keep blood moving through the heart in the right direction.
The aortic valve and pulmonic valve are located between the ventricles and the major blood vessels leaving the heart. 4 heart valves decide the pathway for efficient blood flow through the heart. The heart valves keep blood flowing in one direction through the heart.
Opens to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle. It only has 2 flaps.
The bottom of your foot is connected with your pelvic area. The seven tarsal bones include the calcaneus talus cuboid three cuneiforms and the navicular.
The forefoot contains the five toes phalanges and the five longer bones metatarsals.

What are the parts of the foot called. The thinnest part of your foot usually found towards its center is known as the waistline. This part of the foot has a rough pyramidal shape which creates the arches. The lateral column is stiffer and includes the calcaneus cuboid and the 4th and 5th metatarsals.
Its made up of 4 bones. In humans the foot is one of the most complex structures in the body. Parts of your foot correlated with the stomach are found above the waistline.
The soleus is the lower muscle of the calf. The midfoot is where all three cuneiform bones the medial the intermediate and the lateral cuneiform bones. 26 bones a quarter of the bones in your body.
The medial column is more mobile and consists of the talus navicular medial cuneiform 1st metatarsal and great toe. Parts correlated with the intestines are found below. The foot contains.
The foot is a firm platform that support the weight of the body. Parts Of Foot Bones Anatomy Skeleton Pictures Hindfoot Bones Anatomy. It is made up of over 100 moving parts bones muscles tendons and ligaments designed to allow the foot to balance the bodys weight on just two legs and support.
Ligaments are fibrous strands that connect bones. Like already mentioned the hindfoot is the posterior part of the foot. Could not confirm but think its simply called 아치 toe - 발가락 fingers of the foot ball - 발볼.
Heres some information I was able to dig up. The midfoot is a pyramid-like collection of bones that form the. A network of nerves and blood vessels.
The quadratus plantae are the muscles that are located in the sole of the foot. The midfoot is made up of 5 tarsal bones. Bones of the foot as seen from the medial arch side.
Tendons are tough fibers that connect muscles to bones. Columns of the Foot. Head The head is the upper edge of the sail and is attached at the throat and peak to a gaff yard or sprit.
It is made up of many bones including the tarsal bones the metatarsal bones and the phalanges described in more detail below. The talus is the lower portion of the ankle joint and it is the. The foot is a part of vertebrate anatomy which serves the purpose of supporting the animals weight and allowing for locomotion on land.
Also known as the heel the calcaneus is the foots largest bone. The feet are divided into three sections. Nerves travel throughout the foot providing feeling.
The tendons provide a great deal of energy in proportion to their size. Parts of a Foot. The foot is sometimes described as having two columns Figure 3.
For a triangular sail the head refers to the topmost corner. The bones are called the distal phalanx middle phalanx and proximal phalanx. Muscles contract and relax to move the foot.
These make up the toes and broad section of the. A malfunction in any of these parts of the foot can result. Over 100 tendons ligaments and muscles that connect everything together.
Your foot is made up of soft tissue and bones that work together to form a healthy functioning and pain-free foot. Anatomy of the foot Calcaneus heel bone Talus ankle bone Transverse tarsal joint Navicular bone Lateral cuneiform bone Intermediate cuneiform bone Medial cuneiform bone Metatarsal bones Proximal phalanges Distal phalanges Tarsometatarsal joint Cuboid. The big toe has two bones and one joint.
The bones of the foot are organized into rows named tarsal bones metatarsal bones and phalanges. The midfoot Bones Anatomy. Finally the hindfoot is the area occupied by the heel and.
These muscles are very important but it is actually the tendons that play the most vital role in the movement of the foot. The top of all sails is called the head the leading edge is called the luff the trailing edge is the leech and the bottom edge is the foot. Each of these components works together to help the body with balance support and mobility.

