The leading strand is created continuously making one long strand. A sugar molecule a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base.

The Structure Of Dna By Ron Vale Genetics The Structure Of Dna
Each daughter DNA molecule is composed of one parental strand and one new strand Which of the following structural characteristics of DNA explains its ability to store genetic information.
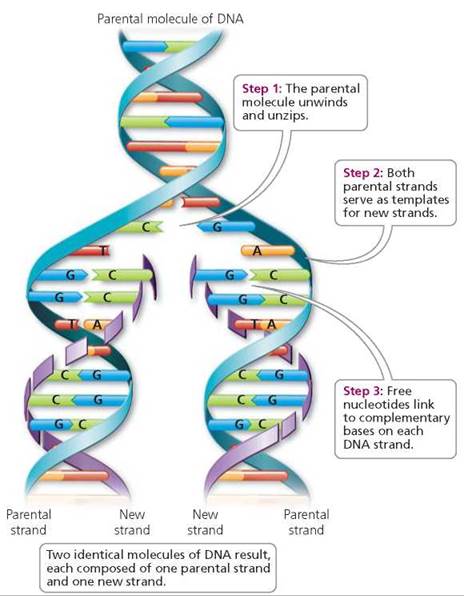
What is the new strand of dna called. The clusters are provided by an enzyme called DNA primase which is a type of dependent-RNA polymerase DNA. The nitrogenous base of a DNA nucleotide can be one of four different molecules. The enzyme joins nucleotides to synthesize a new complementary strand of DNA.
The two strands of DNA run in opposite directions to each other and are thus antiparallel. The process of replication that is the formation of new DNA strands is carried out by a class of enzymes called DNA polymerases. The short lagging strand fragments are called Okazaki fragments.
This sort of DNA replication is continuous. The continuously synthesized DNA strand is called the leading strand and the discontinuously synthesized strand is called the lagging strand. This short segment is called the primer which consists of nine to twelve nucleotides.
The double-stranded DNA molecule is split apart and RNA Pol binds to one strand which it will read and copy. These building blocks are made of three parts. A phosphate group a sugar group and one of four types of nitrogen bases.
Lagging Strand-----There is the lagging strand and the leading strand when DNA is replicated at the fork. The leading strand is the strand of new DNA which is synthesized in the same direction as the growing replication fork. The sugar in DNA is 2-deoxyribose which is a pentose five- carbon sugar.
Each strand of DNA is a polynucleotide composed of units called nucleotides. DNA replication is called semiconservative because each new DNA molecule is made up of one original and one new strand. The principal enzyme involved in DNA replication is called DNA polymerase.
The sugar in DNAs nucleotides is called deoxyriboseDNA is an abbreviation for deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is made of chemical building blocks called nucleotides. RNA molecules use a different sugar called ribose.
This strand is called the template strand or the anti-sense. Each DNA strand of a progenitor cell serves as a. The lagging strand is made of many small fragmentspieces called Okazaki fragments and is generated discontinuously not as one long strand but pieces.
These strands of DNA are called chromatin. To form a strand of DNA nucleotides are linked into chains with the phosphate and sugar groups alternating. A biopolymer comprising multiple linked nucleotides as in DNA is called a polynucleotide.
Similarly what does each DNA strand represent. Attached to each sugar is one of four types of nucleobases informally bases. Why is DNA replication called semi-conservative.
A nucleotide has three components. The lagging strand is the strand of new DNA whose direction of synthesis is opposite to the direction of the growing replication fork. Which of the following builds new strands of DNA the process synthesizes a short range of RNA to an available DNA strand.
Sign in to download full-size image Figure 2. It is done by an enzyme called RNA Polymerase RNA Pol. Remember that during interphase the DNA is contained in the nucleus and consists of very long strands of DNA.
The two DNA strands are also known as polynucleotides as they are composed of simpler monomeric units called nucleotides. The DNA component the team identified is called the intercalated motif i-motif structure which was first discovered by researchers in the 1990s but up until now had only ever been witnessed in vitro not in living cells. RNA Pol only reads one of the two DNA strands as it makes the RNA molecule.
The backbone of the DNA strand is made from alternating phosphate and sugar groups. Adenine A guanine G thymine T and cytosine C.
This allows the 3 billion base pairs in each cell to fit into a space just 6 microns across. This allows the 3 billion base pairs in each cell to fit into a space just 6 microns across.

Dna Strand An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
How DNA is packaged in cells influences the activity of our genes and our risk for disease.

How small is a strand of dna. Select all the observations of Chargaffs rule. Unlike the small cages in London the cages in Italy were much larger and mimicked the environment in sub-Saharan Africa including temperature humidity and even the timing of sunrise and sunset. Elucidating this process will help researchers in all areas of health care from cancer and heart.
If you stretched the DNA in one cell all the way out it would be about 2m long and all the DNA in all your cells put together would be. The four types of nitrogen bases found in nucleotides are. Elucidating this process will help researchers in all areas of health care from cancer and heart.
Click to see full answer. A strand of human DNA is 25 nanometers in diameter There are 25400000 nanometers in one inch A human hair is approximately 80000- 100000 nanometers wide A single gold atom is about a third of a nanometer in diameter. Although each individual nucleotide is very small a DNA polymer can be very large and may contain hundreds of millions of nucleotides such as in chromosome 1.
Replication Bubbles _____ chromosomes have many bubbles. A strand of DNA Im assuming you mean double-stranded DNA rather than single-stranded is 2 nm in diameter - thats 2 billionths of a metre. The human genome comprises the information contained in one set of human chromosomes which themselves contain about 3 billion base pairs bp of DNA in 46 chromosomes 22 autosome pairs 2 sex chromosomes.
This mitochondrial DNA is more like bacterial DNAa single long circular piece of DNA made up of two strands of DNA. Get FREE solutions to all questions from chapter SAMPLE PAPER 2019. - Base pairs project toward the middle of a DNA strand.
As the TWO DNA strands open what forms. Watch complete video answer for A small stretch of DNA strand that codes for a poly of Biology Class 12th. Unlike the small cages in London the cages in.
A new strand of DNA. Adenine A thymine T guanine G and cytosine C. The total length of DNA present in one adult human is.
The leading strand is a new strand of DNA that is synthesized in a single continuous chain that starts at the 5 end and finishes at the 3 end. Chromosome 1 is the largest human chromosome with approximately 220 million base pairs and would be 85 mm long if straightened. How long is a single strand of DNA.
DNA exists as a double-stranded structure with both strands coiled together to form the characteristic double-helixEach single strand of DNA is a chain of four types of nucleotidesNucleotides in DNA contain a deoxyribose sugar a phosphate and a nucleobaseThe four types of nucleotide correspond to the four nucleobases adenine cytosine guanine and thymine commonly. How DNA is packaged in cells influences the activity of our genes and our risk for disease. How An Altered Strand Of DNA Can Cause Malaria-Spreading Mosquitoes To Self-Destruct.
If you stretched the DNA in one cell all the way out it would be about 2m long and all the DNA in all your cells put together would be about twice the diameter of the Solar System. Once the DNA has been seperated into 2 strands another enzyme _____ reads the DNA strand and attaches the correct base nucleotide. Your DNA is arranged as a coil of coils of coils of coils of coils.
You cant resolve something that fine with your eyes or even a light microscope even one of the latest super-resolution microscopes would struggle to resolve down to. The order or sequence of these bases determines what biological instructions are contained in a strand of DNA. Eukaryotic _____ chromosomes have a single bubble.
Select all of the following that are small single-ringed organic bases known as pyrimidines in DNA. - The amount of A equals the amount of T. Aptamers Apts are small single-stranded DNA or RNA sequences of oligonucleotides 2080 nucleotides that can fold into unique tertiary conformations capable of binding proteins phospholipids acid nucleic or CHs expressed by target cells.
How an altered strand of DNA could cause malaria-spreading mosquitoes to self-destruct. To form a strand of DNA nucleotides are linked into chains with the phosphate and sugar groups alternating. Listen 347 347.
DNA polymerase reads the 3-5 template strand to synthesize the complimentary leading strand from 5-3. - cytosine - thymine.