The structure of a hydrophytic leaf differs from a mesophytic leaf due to selective pressures in the environment -- water is plentiful so the plant is more concerned with staying afloat and preventing herbivory. The exchange of oxygen carbon dioxide and water vapors between the leaf cells.

A Labelled Diagram Of A Leaf Microscopic Photography Plant Cell Diagram
Ii Leaf-blade is enriched with reticulate venation.
Labelled structure of leaf. Labeled diagram a leaf midrib this just means central vein within the leaf all the other veins sprout off of it blades these generally are long flat and have a good surface area to capture the maximum amount of sunlight nodes this is the exact spot where the leaf connects itself ot the stem bbc gcse bitesize inside the leaf inside the leaf higher tier you should. On the right side of the image the layers of tissue are labeled from the upper surface of the leaf to the lower. I leaf apex the tip of the leaf blade ii leaf margin the edge of the leaf and iii leaf veins the small channels or capillaries which.
Stem - also called the axis the main support of the plant. Observe a prepared slide of a hydrophyte such as Nymphaea commonly called a water lily. The leaf base is also called as hypopodium.
The thin stalk below the lamina is the petiole. The veins have both xylem and phloem elements which are continuous. Neat Labelled Diagram Of Internal Structure A Leaf And Stomatal Apparatus Brainly In Describe The Internal Structure Of A Dorsiventral Leaf With Help Labelled Diagrams Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community Schematic Transverse Section Through A Dicotyledon Leaf Indicating The Scientific Diagram Internal Leaf Structure Biology Class 11 Ncert Solutions Chapter 6.
I It is green compressed with a wide lamina. The lamina part of the leaf is called as epipodium. A typical leaf of Ficus religiosa pipal has a broad thin flat structure called the lamina.
Labelled Diagram Of A Leaf. Leaves are classified into mainly two types based on their structure dorsiventral and isobilateral. Note the thin epidermal layer.
It is further divided into three parts. The lower of the leaf is called the lower epidermis. It is noticeably differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma.
Masuzi May 26 2020 Uncategorized 0. It attaches the leaf to the plant. Leaf is a lateral flattened structure borne on the stem.
A typical leaf or phyllopodium has 3 parts leaf base petiole and lamina. Palisade cells are column-shaped and packed with many chloroplasts. The upper epidermis of the leaf is sealed by a thick waxy cuticle.
Leaf Structure Transport Reproductive Strategies PDF 檔案Plants. Leaves stems and roots are organs consisting of different types of tissues Plant leaves are the main organ for photosynthesis. The lower epidermis has many stomata.
Parts of a Leaf. Stipule - the small paired appendages sometimes leaf-life that are found at the base of the petiole. It is the thin flat part of the leaf that is typically green in color.
The petiole part of the leaf is also called as mesopodium. Leaves originate from shoot apical meristems and are arranged in an acropetal order. Parts of a Leaf.
There are no stomata present in the upper epidermis. A typical leaf consists of three main parts-1- Leaf base hypopodium 2. Leaf-blade or Lamina.
Required fields are marked Comment Save my name email and website in. Petiole - a leaf stalk. A leaf has two main parts.
In all leaves there is no distinction between protophloem older phloem and metaphloem new phloem. Read this article to learn about Structure of a Typical Leaf. They are the most important vegetative organs for photosynthesis.
It is the basal part of leaf by which it is attached to the node of the stem or its branches. There is another type of leaf called unifacial like Allium. Parts Of A Leaf Labelled Diagram.
Identifying characteristics of the internal structure of dorsiventral or dicot leaf. A Labelled Diagram Of A Leaf New Holland Skid Steer Parts Diagram Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis Venn Diagram Posted in Diagram Leave a Reply Cancel reply Your email address will not be published. It is composed of elongated cells arranged in two layers.
Parts of a leaf their structure and describe the structure of leaf with draw the labelled diagram of parts a draw a labelled diagram of internal. Midrib - the central rib of a leaf - it is usually continuous with the petiole. 1 Petiole- the stalk that supports a leaf in a plant and attaches the leaf blade to the stem.
Iii Mesophyll tissue is present and is composed of palisade parenchyma and spongy parenchyma. Plant structure Flowering plants have a basic structure. Light absorption happens in the palisade mesophyll tissue of the leaf.
The lamina possesses a network of veins. WJEC AS Biology Plants. A unifacial leaf is cylindrical in outline so there is no distinction between the upper and lower surface.
Cross section of a hydrophytic leaf. Parts Of A Leaf Their Structure And Functions With Diagram. It develops at tha node and bears a bud in its axil.
As we discussed above that there are three major leaf parts which are as follows. Each stoma has an opening and two bean-shaped guard cells. 2 Lamina- the green flat part of a leaf that is specialized for photosynthesis.
They are arranged closely together so that a lot of light. Just below the epidermis are several layers of tightly packed cells called the hypodermis. The upper layer of a leaf is called the upper epidermis.
The foliage leaf consists of three parts namely leaf base petiole and lamina. The axillary bud later develops into a branch. Beneath the hypodermis the palisade and spongy mesophylls are arranged as in a mesophytic leaf.
The cerebrum is the large main part of the brain and serves as the thought and control center. Studies published here integrate data spanning from molecular cellular developmental and system architecture to the neuroanatomy of behavior and cognitive functions to clinical neuroanatomy and brain dysfunction.

Brain Structure And Function Home
Brain Structure and Function IF is decreased by a factor of 032 and approximate percentage change is -895 when compared.

Brain structure and function impact factor. Brain connectivity connectomics resting. 2018 Impact Factor 3709. The ISSN of Brain Structure and Function journal is 18632653 18632661.
It is thought that this determination is based on how huge an emotional response an event evokes. Brain Structure and Function is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on brain structure-function relationshipsIt was established in 1891 as Anatomische Hefte renamed first Zeitschrift für Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte in 1921 and then Anatomy and Embryology in 1974 before obtaining its current name in 2007. 2019 Impact Factor 3622.
Volker Coenon Universität Freiburg Keywords. 2016 Impact Factor 3789. 2009 Impact Factor 4673.
By better understanding how different parts of the brain function you can also better appreciate how disease or injury may impact certain functions. Brain Structure and Function Impact Factor 371 IF number of citations detailed analysis and journal factor. Function of cortical microcircuits neuronal.
3 in the past 20 years our ability to quantify this atrophy has improved using structural brain imaging technology computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging mri. The human brain is remarkably complex and researchers are still working toward understanding many of the mysteries of how the mind works. MFB human reward circuitry subthalamic nuclei networks.
The human brain is the most complex of all living constructions processing sensory information while. Brain Structure Function publishes research that provides insight into brain structurefunction relationships. Socioeconomic factors impact a childs brain structure.
Studies of the mammalian nervous system. An International Standard Serial Number ISSN is a unique code of 8 digits. Manuscripts with focus on the spinal cord or the peripheral nervous system are not accepted for publication.
The cerebral cortex is responsible for many higher-order brain functions such as sensation perception memory association thought and voluntary physical action. The Brain Structure and Function Impact Factor IF measures the average number of citations received in a particular year 2020 by papers published in the Brain Structure and Function during the two preceding years 2018-2019. 11 rows Brain Structure.
Neuroscience Peer Review ConsortiumBrain Structure and Function is a member of the Neuroscience Peer Review Consortium NPRC an alliance of neuroscience journals that have agreed to share manuscript reviews at the authors request. Studies published here integrate data spanning from molecular cellular developmental and systems architecture to the neuroanatomy of behavior and cognitive functions. Brain Structure Function publishes research that provides insight into brain structurefunction relationships.
SJR acts as an alternative to the Journal Impact Factor or an average number of citations received in last 2 years. The best quartile for this journal is Q1. If you think that you are experiencing symptoms of a brain.
18 the first two of these are most important with regard to ageing. The brain role as part of the Central Nervous System is to regulate most functions of human body including vital functions such as heart rate or breathing basic functions like being hungry sleeping or sexual instinct also complex functions like speaking thinking remembering etc. 2013 Impact Factor 3567.
Genomic imaging genetic factors structural and functional MRI. 2014 Impact Factor 3808. It is published by Springer ScienceBusiness Media.
Brain Structure And Function Impact Factor. Neuroanatomy diffusion tensor imaging DTI deep brain stimulation DBS medial forebrain bundle mfb rodent. The amygdala is also responsible for determining what memories are stored and where the memories are stored in the brain.
The impact factor IF 2019 of Brain Structure and Function is 3298 which is computed in 2020 as per its definition. 2011 Impact Factor 6759. It is involved in the processing of emotions such as fear anger and pleasure.
2012 Impact Factor 8598. 2478 Read 1100 articles with impact on ResearchGate the professional network for scientists. Studies published here integrate data spanning from molecular cellular developmental and systems architecture to the neuroanatomy of behavior and cognitive functions.
2017 Impact Factor 4107. Brain Structure and Function Citations. 2015 Impact Factor 4091.
Brain Structure and Function. The NPRC has been formed to expedite the review process to speed the publication of research reports and to reduce the overall burden on peer. This journal has an h-index of 82.
Studies published here integrate data spanning from molecular cellular developmental and systems architecture to the neuroanatomy of. Dirk Feldmeyer Forschungszentrum Jülich Keywords. Brain Structure And Function Impact Factor.
20202021 Impact Factor 327. Brain Structure Function publishes research that provides insight into brain structurefunction relationships. The Brain Structure and Function Impact Factor IF measures the average number of citations received in a particular year 2020 by papers published in the Brain Structure and Function during the two preceding years 2018-2019.
Function publishes research that provides insight into brain structure-function relationships. The amygdala is involved in autonomic responses. 2010 Impact Factor 5305.
Explain the structure of a typical dicotyledonous seed with a neat labelled diagram. The pointed beak like end of the seed has a minute pore called micropyle.
Diagram Of Embryo Of Dicot Seed With Labeling Science How Do.

Labelled diagram of structure of seed. The funiculus disappears leaving a scar called hilum. Structure of seed diagram. Get the answers you need now.
Plants seed structure an introduction biology article. Draw the labelled diagram of germination of pollen on stigma seed germination structure of seed - 15130409. Solved 7 Label The Parts Of The Seed In The Diagram Belo.
The seed surface may be smooth wrinkled striate ribbed furrowed reticulate tuberculate alveolate hairy and pulpy or having patterns like finger prints. It facilitates entry of oxygen and water into the seeds during germination. 3 Seed Structure Sexual Reproduction In Plants.
Explain the structure of a typical dicotyledonous seed with a neat labelled diagram. In favourable conditions the seed can grow and become a fully independent plant bearing flowers and seeds during its life cycle. The one which forms the shoot tip is called plumule and the portion at the lower end which forms the root tip is called radicle.
It consists of a tough coat or testa enclosing an embryo which is made up of a plumule a radicle and one or two cotyledons. A seed develops from an ovule after fertilization. The whole content is enclosed within a protective cover seed coat.
Parts of a Seed Diagram A typical seed consists of three main parts. It consists of two layers-outer testa and inner tegmen. Labelled diagram of a germinating seed free ebooks.
Some of the worksheets for this concept are Bean seed Food seed coat The anatomy of a bean seed Seed diagram for kids Getting to know you Lesson 4 weve bean growing anatomy of germination summary Structures of seed plants. Explain the structure of a typical dicotyledonous seed with a neat labelled diagram. Getting Image Please Wait.
Structure of a Cicer seed as an example for Dicot seed The mature seeds are attached to the fruit wall by a stalk called funiculus. Draw labelled diagrams of the structure ofseed of 1 gram. 1 draw a neat labelled diagram of a germinated seed and.
Parts of a seed and their functions cropsreview com. Seed structure diagram stock image c009 3021 science. The seed coat is made up of an outer layer called testa and.
There are hundreds of variations in the seed size shape colour and surface. If a soaked seed is gently pressed a. Brassicaceae - Lepidium sativum as model system in seed biology.
Answer Gram seed is shown in the above portion and the maize seed is shown in the below portion. In mature seeds of Lepidium sativum garden cress the embryo is surrounded by 1-2 cell layers of endosperm. Draw The Labelled Diagram Of The Following I Gram Seed Ii.
It also provide mechanical support and storage. Labeled diagram of a seed youtube. The tegmen is thin membranous and whitish and remains fused with testa.
Draw labelled diagram of the following i Gram seed ii VS. 1 seed coat 2 endosperm and 3 embryo. The seeds range in size from tiny dust particles as found in some orchids to large double-coconuts.
The structure labeled X is xylem. Testa is thick and brownish. Below the hilum a small pore called micropyle is present.
1 Seed Coat They are the protective outer covering of a seed that is usually hard thick and brownish in color. Avail 25 off on study pack. Process of seed germination tutorvista.
It has two ends. Leave a Comment Uncategorized Uncategorized. Seed Structure Diagram Wiring Diagram Echo.
Endospermic seed structure Eudicots. Xylem is a vascular tissue found in vascular plants that is responsible for transporting water from the roots to other parts of the plant. Seed Diagram - Displaying top 8 worksheets found for this concept.
We found that Lepidium seeds exhibit as tobacco a two-step germination process with distinct testa rupture and endosperm rupture.
Light enters the eye through the cornea. This leaderboard is currently private.
Human Eye Anatomy Parts And Structure Online Biology Notes.
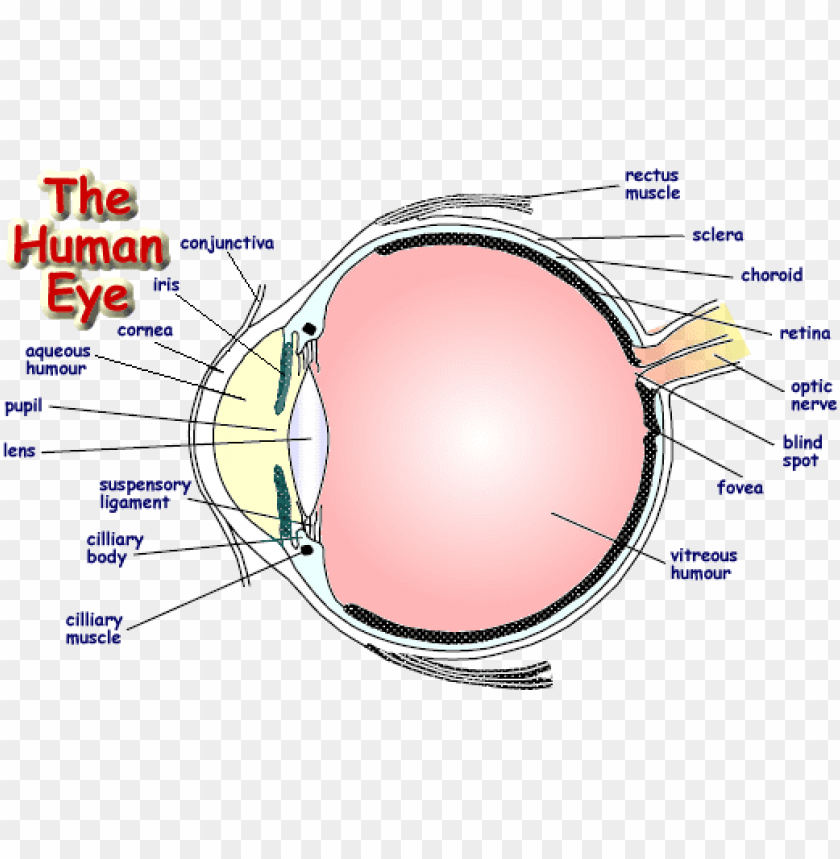
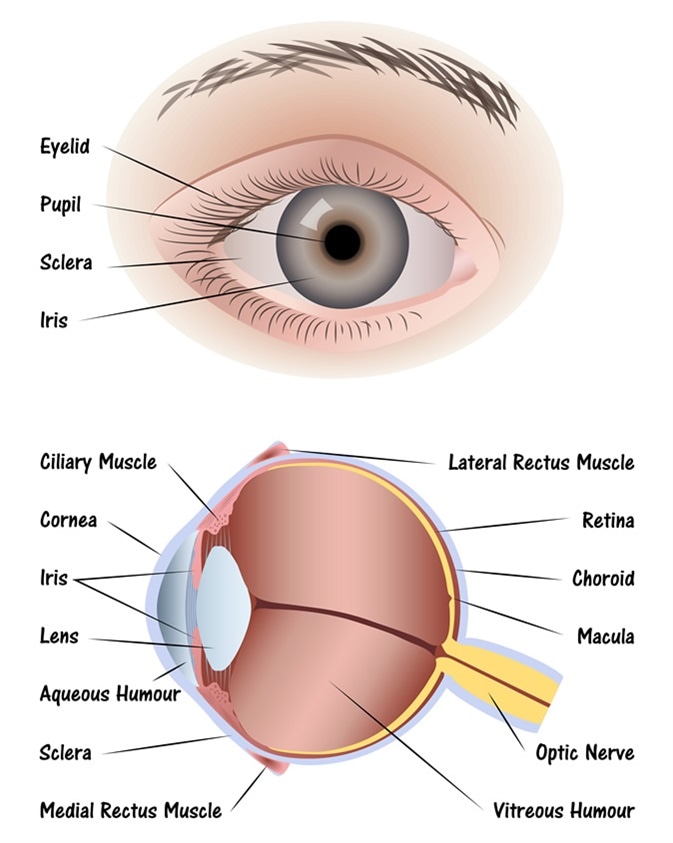
Labelled structure of human eye. This means that it regulates how much light gets into the eye. Its wall has three distinct layersan outer fibrous layer a middle vascular layer and an inner nervous layer. Anatomy parts and structure.
There are 6 sets of muscles attached to outer surface of eye ball which helps to rotate it in different direction. Gcse Biology Structure Of The Eye. Human eye is spherical about 25 cm in diameter.
Diagram of the eye diagram of eyeball cross section of human eye section of human eye cross section eye cross section of eye anatomy of the eye eye parts human eye diagram of eye. Structure of Human Eye. It directly covers your iris and pupil providing a layer of.
The spaces within the eye are filled with fluids that help maintain its shape. The external layer consists of the and sclera cornea. Share Share by Krishmatalwar.
The pupil is a small opening in the iris. Labelled Diagram of Human Eye The eyes of all mammals consists of a non-image-forming photosensitive ganglion within the retina which receives light adjusts the dimensions of the pupil regulates the availability of melatonin hormones and also entertains the body clock. Structure And Functions Of Human Eye With Labelled Diagram.
Saland Vision Diagram Of The Eye Dallas. Ocr Gcse Biology The Eye Quiz. Show more Show less.
Internal parts of the eye Cornea. Further refracts light to focus it onto the retina. Controls how much light enters the pupil.
The pupils function is to adjust the amount of light entering the eye. It is situated on an orbit of skull and is supplied by optic nerve. The eye is the photo-receptor organ.
Gcse Igcse Biology By Syllabus Points. These include the eyebrows the eyelids and eyelashes the conjunctiva and the lacrimal apparatus. This leaderboard is disabled as your options are different to the resource owner.
6513 human eye diagram stock photos vectors and illustrations are available royalty-free. This iris is made from connective tissue and muscle surrounding the pupil and its structure pattern and colour are just as unique as your fingerprint. The outer covering of the eye is called sclera.
Free Unlabeled Eye Diagram Download Free Clip Art Free Clip Art. The cornea is responsible for the maximum refraction of light incidents on the eye. The iris controls the size of the pupil which is the opening that allows light to enter the lens.
The light then passes through the pupil the circular opening in. The sclera is a dense protective white covering that physically supports the internal structures of the eye. A dark muscular.
See human eye diagram stock video clips. Refracts light - bends it as it enters the eye. Cornea accounts for two-thirds of.
The cornea is the clear surface at the front of your eye allowing light to enter the eye. Anatomically the eye comprises two components fused into one. It is the outer covering a protective tough white layer called the sclera white part of the eye.
INTERNAL STRUCTURES OF THE EYE The eyeball is composed of three separate coats or layers Fig. Light is focused by the lens and goes through. The iris controls the size of the pupil.
It is continuous anteriorly with the transparent cornea the win-dow of the eye. The Accessory Structures of the Eye. Light enters the eye by passing through the transparent cornea and aqueous humor.
The function of the Human Eye Light waves of an object enter the eye first through cornea a clear dome-shaped structure the front of the eye. The front transparent part of the sclera is called cornea. The rays of light enter this layer.
Structure of Human Eye. It is the clear transparent anterior portion of the external coat of the eyeball. Human Eye Diagram Image will be Uploaded Soon The structure of the human eye is shown above in the image Parts of the Human Eye.
External components include structures which can be seen on the exterior of the eye and internal components include structures. The human eye is a roughly spherical organ responsible for perceiving visual stimuli. It consists of the following parts.
Structure of Human eye 3 i Cornea. It is a protective tough white layer white part of the eye. It is enclosed within the eye sockets in the skull and is anchored down by muscles within the sockets.
Lens Drawing Eye Picture 2694249 Lens Drawing Eye. Click Share to make it public. A human eye is roughly 23 cm in diameter and is almost a spherical ball filled with some fluid.
The human eye is a part of the sensory nervous system. Anatomy Of The Human Eye. Structure of the Human Eye The eye is a hollow spherical structure about 25 centimeters in diameter.
Hence it does not possess a perfect spherical shape. Try these curated collections. Http Www Gemsclub Org Yahoo Site Admin Assets Docs Sheep Eye Dissection 190121501 Pdf.
The main parts of the human eye are the cornea iris pupil aqueous humor lens vitreous humor retina and optic nerve. This leaderboard has been disabled by the resource owner.
Each kidney is formed of about 1 million nephrons. Leading form the pelvis is a tube called the ureter.

Draw A Neat Labelled Diagram Of Internal Structure Kidney What Is The Function Of Kidney Brainly In
On the superior aspect of each kidney is an adrenal gland.
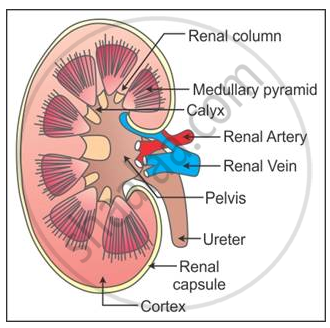
Describe the structure of kidney with labelled diagram. Vessels nerves lymphatics and ureters. Label kidney diagram. Each kidney has nearly one million complex tubular structures called nephrons which are the functional units.
Kidney functions Ultrafiltration of blood selective reabsorption by active transport. Each kidney looks like the kidney bean and the renal hilum is the entry and exit site for structures servicing the kidneys. Labeled Diagram of the Human Kidney.
An inner lighter area called Medulla. The kidneys are two in number which are situated one on each side of the verteral column and in-front of the last ribs. The right kidney is placed slightly lower- than the left due to the presence of liver which occupies much space on the right side.
Make sure you can label the diagram showing the relative positions of the kidneys ureters bladder and urethra. The spellings of the ureter and urethra are really important. A kidney is composed of an enormous number of uriniferous tubulesThey are also known as nephrons or renal tubules or kidney tubules.
In addition they also play an important role in maintaining the water balance of our body. The average kidneys are about 150 gm in males and 135 gm in females. After reading this article you will learn about the structure of the kidney.
Name the cavity in which the kidney sits. With the help of well labelled diagram describe the structure of nephrons. A kidney is a bean-shaped organ that is reddish-brown in color.
Q4 Describe the structure of the kidney with the help od a l LIDO. I Glomerular filtration - Urine formation begins when the blood is filtered by the glomerulus and enters the Bowmans capsule and the glomerular filtrate is formed. The process of urine formation in kidneys include the following steps.
They lie on the posterior abdominal wall. A thin connective tissue called the renal capsule surrounds each kidney. STRUCTURE OF THE NEPHRON At one end of the nephron is a cup-shaped Bowmans capsule about 200µm in diameter located in the outer region cortex if the kidney.
The microscopic structure of the kidney is formed of millions of tubules called renal tubules or nephrons. The nephron is one of the most important parts of our body and also one of the smallest functioning units. The bean-shaped kidneys have an outer convex side and an inner concave side called the renal hilus where the renal artery vein and ureter are found.
This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of kidney. Image of a kidney and nephron with the major structures labeled. Kidney dissection Learning outcomes Describe the external features of the kidney Describe the position of the kidneys in the body and relationships with blood supply and rest of urinary system Draw and label LS kidney Recognise different parts of the kidney Make a drawing to scale 6.
Nephrons are the structural and functional units of the kidney. A kidney is composed of an enormous number of uriniferous tubulesThey are also known as nephrons or renal tubules or kidney tubulesNephrons are the structural and functional units of the kidneyEach kidney is formed of about 1 million nephronsNephrons are held together by a connective tissueStructure of nephron. The human kidneys house millions of tiny filtration units called nephrons which enable our body to retain the vital nutrients and excrete the unwanted or excess molecules as well as metabolic wastes from the body.
Structure of a kidney The kidney has 3 main parts. Q4 Describe the structure of the kidney with the help od a labelled diagram. Each kideney is covered by semi-liquid fatty tissue called adipose capsule.
In LS the kidney shows two regions within the capsule. Gross Structure Of Kidney Kidneys with blood vessels the one on to right is a longitudinal section of the kidney. Nephrons have two parts glomerulus and the renal tubule.
The invagination contains a. The kidneys are slightly protected by the ribs and are surrounded by fat for protection. This capsule maintains the kidneys shape and protects the inner tissues.
The cortex medulla and pelvis. Dehydration a blockage in the urinary tract or kidney damage can cause acute renal failure which may be. This increases the blood pressure within the glomerulus helps in the filtration.
The afferent arteriole entering the glomerulus is wider than the efferent arteriole in diameter. An outer darker area called Cortex. Figure 2511 Kidneys.
Q4 Describe the structure of the kidney with the help od a labelled diagram. Section through the kidney to show different regions The kidneys are composed of. It has a dimension of 11 cm in length 6 cm in width and 3 cm in thickness.
Outer covering of this capsule is made up of tough fibrous connective tissue called renal fascia. Outer renal cortex and inner renal medulla. Click to find video solution.
It is like a ball which has been pressed in on one side. A kidney is composed of an enormous number of uriniferous tubulesThey are also known as nephrons or renal tubules or kidney tubulesNephrons are the structural. They are held in.