Arcuate or fan-shaped - the land. Upon observation of an Old Age River here is what one might see.
Anatomy Of A Delta The Foundation Of New Land Restore The Mississippi River Delta
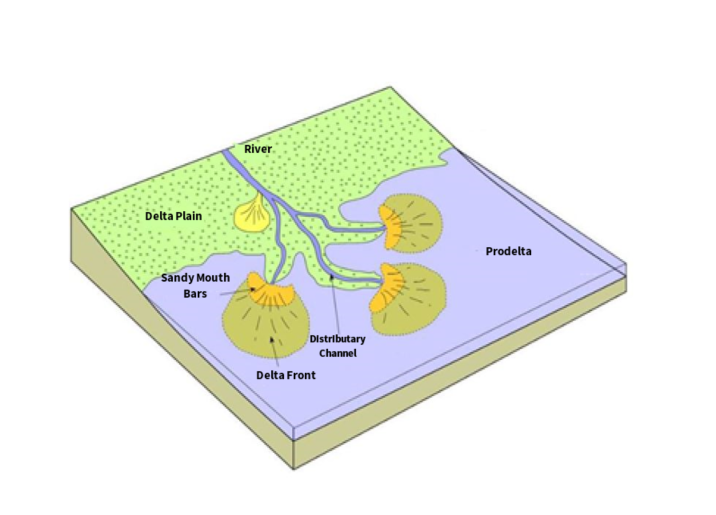
Deltas are formed when river water comes into contact with a standing body of water making the river lose its velocity.

Labeled diagram of a river delta. These river diagrams help to explain the geography topic of rivers. When a river enters a lake it is called a lacustrine delta. The river flows down a very shallow gradient slope.
Deposited material divides the river into smaller distributaries. They are fundamentally features of river deposition not marine deposition. When more of the flood plain between the individual distributary channels is exposed above the sea level the delta displays lobate shape.
Wave-dominated delta shorelines are more regular assuming the form of gentle arcuate protrusions and beach ridges are more common eg the Nile River delta or Niger River delta. The velocity of the water and capacity of a river or stream to hold sediment in suspension suddenly drop when it enters the relatively still body of water such as a lake or the ocean. Thus the stream dumps its sediment load here and the resulting deposit is known as a delta.
Through looking at these diagrams it is easier to understand the nature of V-shaped valleys the river ordering system the water cycle and other aspects related to rivers. Wright and Coleman 1972 showed that the nature of the subaqueous profile of the delta determines the attenuation of wave power and thus influences the resulting shape of the delta. This diagram of a river resource is perfect for Geography lessons.
This then causes it to dump its load. Those ideas were extended into a ternary diagram. Children can practise identifying the parts of a river with labels.
The term delta was first used for these deposits by Herodotus in the. The colourful diagram of a river requires children to label each feature with the correct terminology. Youll find important terms like tributary bank floodplain.
There are three main types of delta named after the shape they create. This resource complements the Go Teach Label Parts of a River Interactive Activity which can be used on a whiteboard or large screen. 3 Birds foot Delta.
It has been produced by the pupils at. Teach your KS2 children to recognise and name features of rivers using this beautifully detailed labelling activity. A delta is formed when the river deposits its material faster than the sea can remove it.
We like this model of a river system because it has neatly labelled features on it and it has the opportunity to combine knowledge of showing heights on maps using layer shading. This usually occurs when the river joins a sea estuary ocean lake reservoir or in rare cases a slower moving river. Pupils can cut out and position the labels to identify key features - great for class discussion and group collaboration.
Here the breaking waves cause an immediate. Old Age Rivers actually have more distinguishing features to speak of than the Youthful and Mature Rivers do. Formed at the mouth of submerged rivers depositing down the sides of the estuary.
A great combination to really reinforce learning. This practical resource provides pupils with the diagrams and labels needed for them to identify parts of a river. The channel wider than it is deep with a very broad and U-shape due to extensive lateral side-to-side erosion.
Children can practise identifying the parts of a river with labels. Formed when a river. Pupils can cut out and position the labels to identify key features - great for class discussion and group collaboration.
Deposition is enhanced if the water is saline. Geography project idea - Make a 3D River Basin model. Since salty water causes small clay particles to flocculate the meeting of fresh and salt water produces an electric charge which causes clay particles to coagulate and to settle on the seabed.
A river delta is formed at the mouth of a river where the river deposits the sediment load carried by it and drains into a slower moving or static body of water. External delta morphology are qualitative and focused on the relative contributions of rivers waves and tides. Triangle-shaped deltas formed of sands and gravels.
This resource complements the Go Teach Label. Measuring about 40000 sq km our very own Sundarban forms the largest river delta in the world and is formed by the coalescing of two very large rivers the Ganga and the BrahmaputraThis is an also arcuate river delta which features many active short distributaries pushing heavy sediments to their mouthsThere is a cluster of low-lying islands in the Bay of Bengal spread.